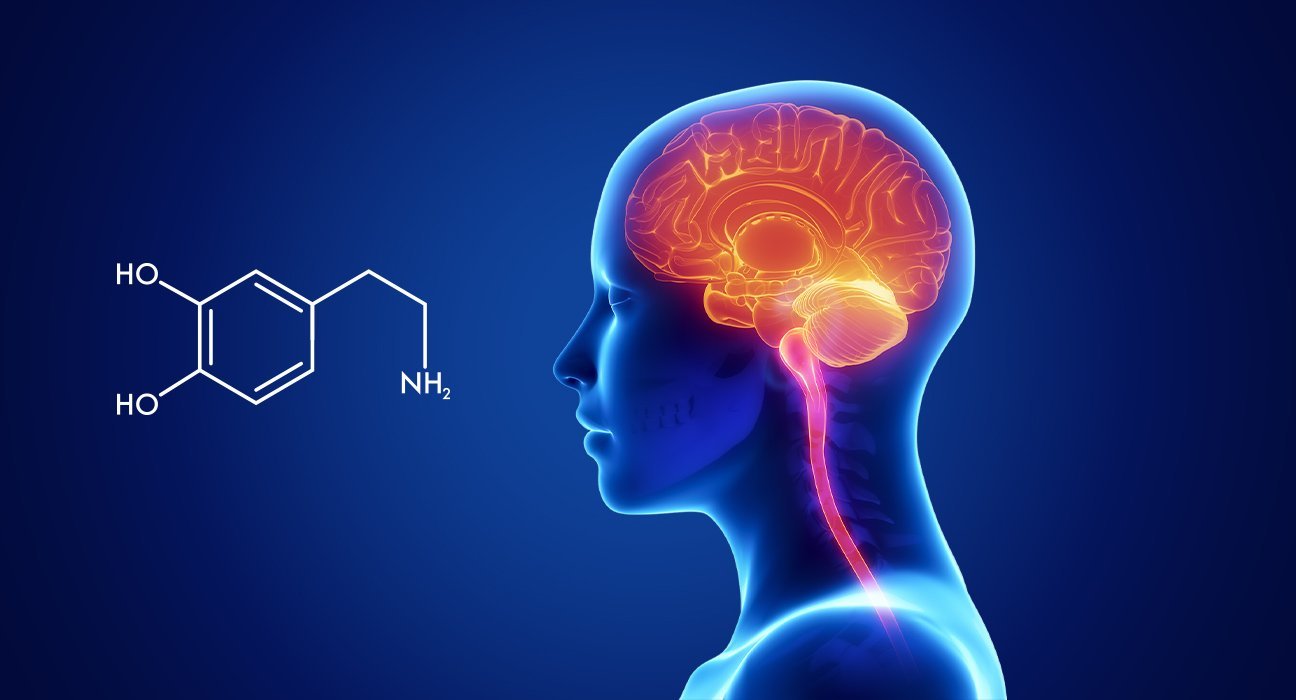
It is a chemical that is released in the brain. It is linked to numerous types of mood disorders and has an impact on the emergence and maintenance of addictions. And Dopamine plays a huge role in the various functioning of the mind.
Attention, Motivation, and Emotion
It plays an important role in attention, motivation, and emotion regulation in the brain. When dopamine levels are optimal, it helps enhance our ability to concentrate on important tasks and filter out distractions. The motivational processes within the brain intricately involve it, and the brain’s reward system relies on it as a key component. We release it when we encounter pleasurable experiences, such as eating delicious food or engaging in enjoyable activities. It also plays an important role in initiating and sustaining motivation. Also, It has a role in the regulation of emotions. It interacts with other neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and norepinephrine, to modulate emotional states. Dysregulation of dopamine in emotional processing has been linked to mood disorders, such as depression and bipolar disorder.
Learning and Creativity
It plays a critical role in learning and creativity as well. It helps reinforce neural pathways that lead to positive outcomes, strengthening the association between stimuli and rewards thereby promoting the learning of new behaviors and the formation of memories. Additionally, researchers have also linked it to creative thinking, and it influences the brain’s ability to make connections between seemingly unrelated concepts, facilitating the formation of new associations and ideas. It promotes divergent thinking, allowing individuals to explore multiple solutions to a problem. However, just like how an excess of anything can be bad, an optimal balance of dopamine is crucial, as both too little and too much dopamine can negatively impact creativity.
Dopamine and Addiction
It plays a crucial role in the development and maintenance of addiction. Substances such as cocaine, amphetamines, and opioids etc can directly or indirectly affect dopamine levels in the brain. The intense euphoria associated with drug use reinforces the connection between drug-seeking behavior and the release of dopamine, driving the cycle of addiction.
Dopamine and Mental Health
Reduced dopamine activity in crucial brain areas involved in motivation and reward is frequently linked to depression. This can result in anhedonia, a diminished ability to experience pleasure, and a lack of motivation. The hallmark of schizophrenia is an overactive dopamine system. In the treatment of these conditions, healthcare professionals commonly use medications, such as antipsychotics and antidepressants, to modulate dopamine levels and restore balance by targeting Its receptors.
To conclude, we can say that Dopamine is an important neurotransmitter that has an important role in the various kinds of functioning of the brain. Dopamine levels play a role not only in the emotional states of individuals. But also affect their learning, creativity, and decision-making to some extent. The emergence and maintenance of addictions are impacted by it, and it is associated with a number of mood disorders.